Installation of TrackMe
Installation Target
TrackMe is a Search Head component only; therefore, it must be deployed only on a target Search Head layer:
Splunk roles |
Required |
|---|---|
Search head |
yes (*) |
Monitoring console |
yes (*) |
Indexer tiers |
no |
Heavy Forwarders |
no |
You can deploy TrackMe on a dedicated Search Head or Search Head Cluster, or alternatively on the machine hosting the Splunk Monitoring Console.
If you choose to install TrackMe on your Search Head layer in a Search Head Cluster (SHC), TrackMe must be deployed through the SHC deployer node.
Indexes Definition
Default Indexes
TrackMe requires at least 4 indexes to be defined. In a distributed context, this usually means defining indexes in your manager node:
Default index name |
Purpose |
Minimal recommended retention |
|---|---|---|
trackme_summary |
TrackMe entities activity such as the state, flipping events, and Smart Status |
3 months |
trackme_audit |
TrackMe modifications and application audit activity |
1 year or more |
trackme_notable |
Notable events are generated by the TrackMe notable alert action |
3 months |
trackme_metrics |
Various metrics are generated depending on the components |
1 year or more (notably to allow long term outliers detection and metrics analytics) |
Indexes are defined by default in the application package:
trackme/default/indexes.conf
Typically:
If TrackMe is running on an “all-in-one” instance, you do not need to define the indexes as the application defines these already (mostly for testing and development purposes).
It is good practice to use Splunk volumes rather than the default SPLUNK_DB variable to define the location of the buckets (which is required when using SmartStore).
Therefore, a typical definition would be:
[trackme_notable]
coldPath = volume:primary/trackme_notable/colddb
homePath = volume:primary/trackme_notable/db
thawedPath = $SPLUNK_DB/trackme_notable/thaweddb
[trackme_summary]
coldPath = volume:primary/trackme_summary/colddb
homePath = volume:primary/trackme_summary/db
thawedPath = $SPLUNK_DB/trackme_summary/thaweddb
[trackme_audit]
coldPath = volume:primary/trackme_audit/colddb
homePath = volume:primary/trackme_audit/db
thawedPath = $SPLUNK_DB/trackme_audit/thaweddb
[trackme_metrics]
coldPath = volume:primary/trackme_metrics/colddb
homePath = volume:primary/trackme_metrics/db
thawedPath = $SPLUNK_DB/trackme_metrics/thaweddb
datatype = metric
Adapt with the volume definitions in your context.
Virtual Tenants Specific Indexes
A core concept of TrackMe is called Virtual Tenants, which provides many powerful features. Part of this concept provides the capability to define a per-tenant specific set of indexes.
Therefore, you can choose to define specific indexes for one or more tenants, and a different set of indexes for other tenants.
This allows TrackMe to comply with any Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) requirements, for instance, to allow a population of users to access specific tenants while another population can access others.
Example: Virtual Tenant indexes definition configuration screen:
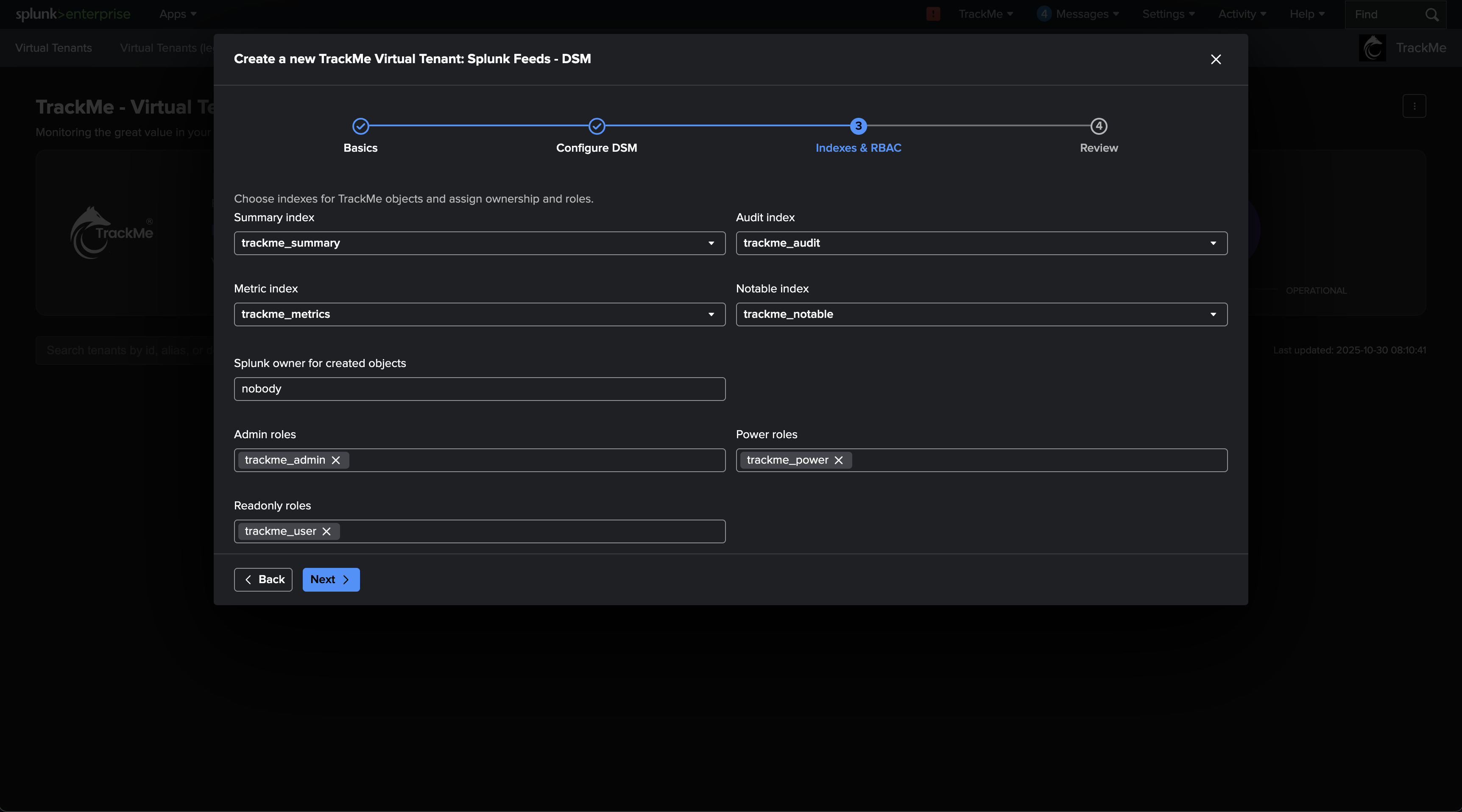
Installing TrackMe
Splunk Enterprise
Installing TrackMe on Splunk Enterprise on-premises deployments depends on the type of deployment.
For standalone instances, refer to: https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/AddOns/released/Overview/Singleserverinstall
For distributed deployments, refer to: https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/AddOns/released/Overview/Distributedinstall
Notes for Older Generations of Splunk (prior to Splunk 9.x)
TrackMe is developed for the latest generation of Splunk software; therefore, some built-in parameters are primarily targeting Splunk 9.x compatible configurations.
If you are running TrackMe on a version prior to Splunk 9.x, you should apply the following customizations:
Create a local/distsearch.conf:
# distsearch.conf
# Avoid the replication to the indexers of the KVstore backup tarball compressed files
[replicationBlacklist]
trackme_backup_tgz = apps/trackme/backup/*.tgz
trackme_backup_dirs = apps/trackme/backup/...
# These lookups do not need to be replicated
trackme_cim_regex = apps/trackme/lookups/trackme_cim_regex.csv
# Machine Learning models: Anomaly detection will generate various ML models files, these are not needed on the indexer layers
trackme_mlmodels = apps/trackme/lookups/__mlspl_*.mlmodel
Notes:
In Splunk 9.x, biased language has been addressed; this stanza became replicationDenylist.
In TrackMe, this stanza prevents ML models files from being unnecessarily replicated to the indexers and being part of the knowledge bundle.
Splunk Cloud
Installing TrackMe on Splunk Cloud relies on Cloud self-services. Refer to:
Upgrading TrackMe
In summary, upgrading TrackMe follows the same process as installation:
In Splunk Enterprise, you will download the updated release, extract the new version, restart the instance if in a standalone Search Head, or apply the SHC bundle if running in an SHC.
In Splunk Cloud, when a new release has been published and vetted, the new version release number appears as upgradable through the application management interface; you will therefore follow the self-services process.
TrackMe implements an automated concept to perform required application-level upgrade procedures, called schema version. See Upgrading TrackMe.