Role Based Access Control and ownership
Least privileges approach in TrackMe
TrackMe uses a strict least privileges approach which avoids any requirements for dangerous or problematic Splunk capabilities, such as list_settings or list_storage_passwords for most of its operations.
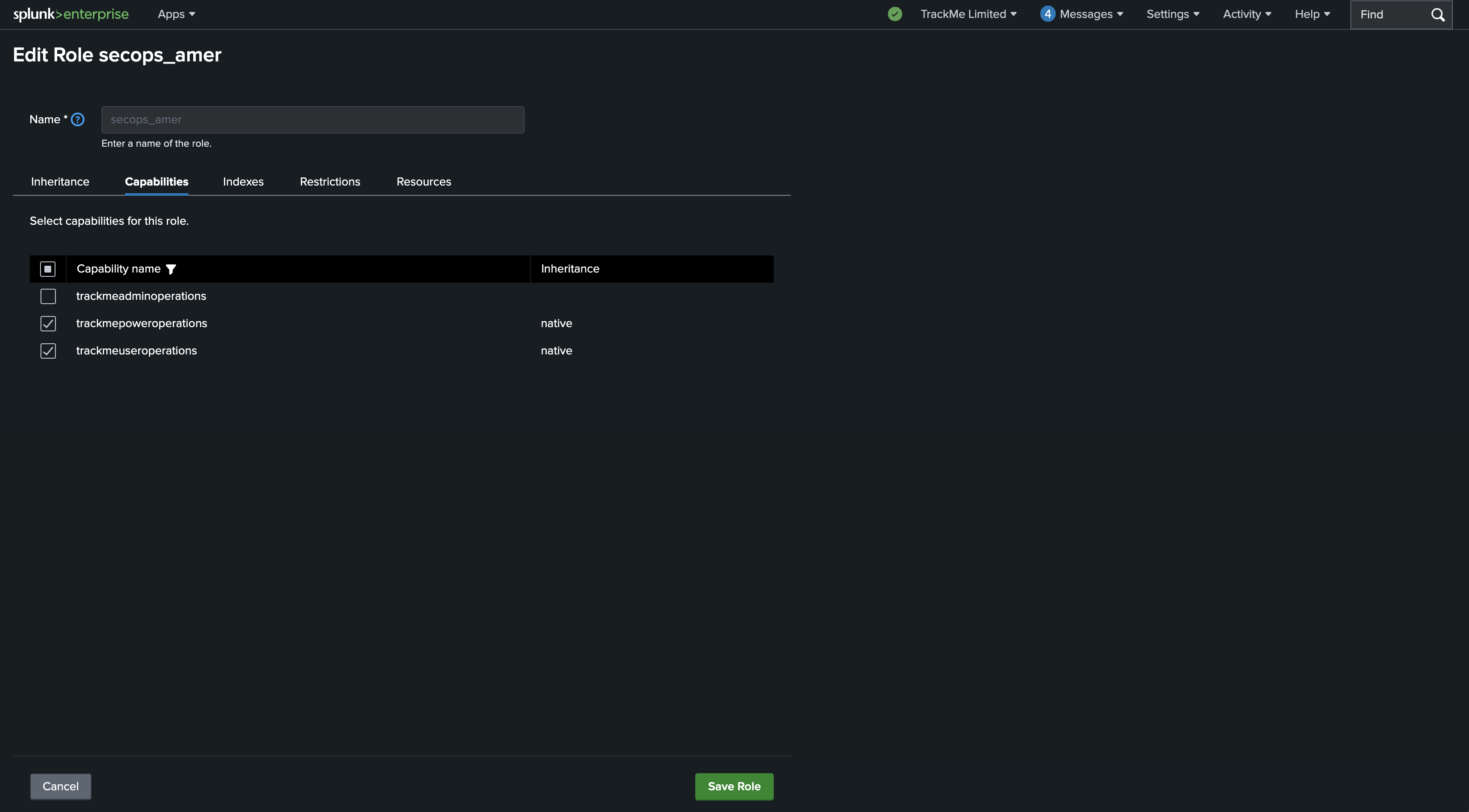
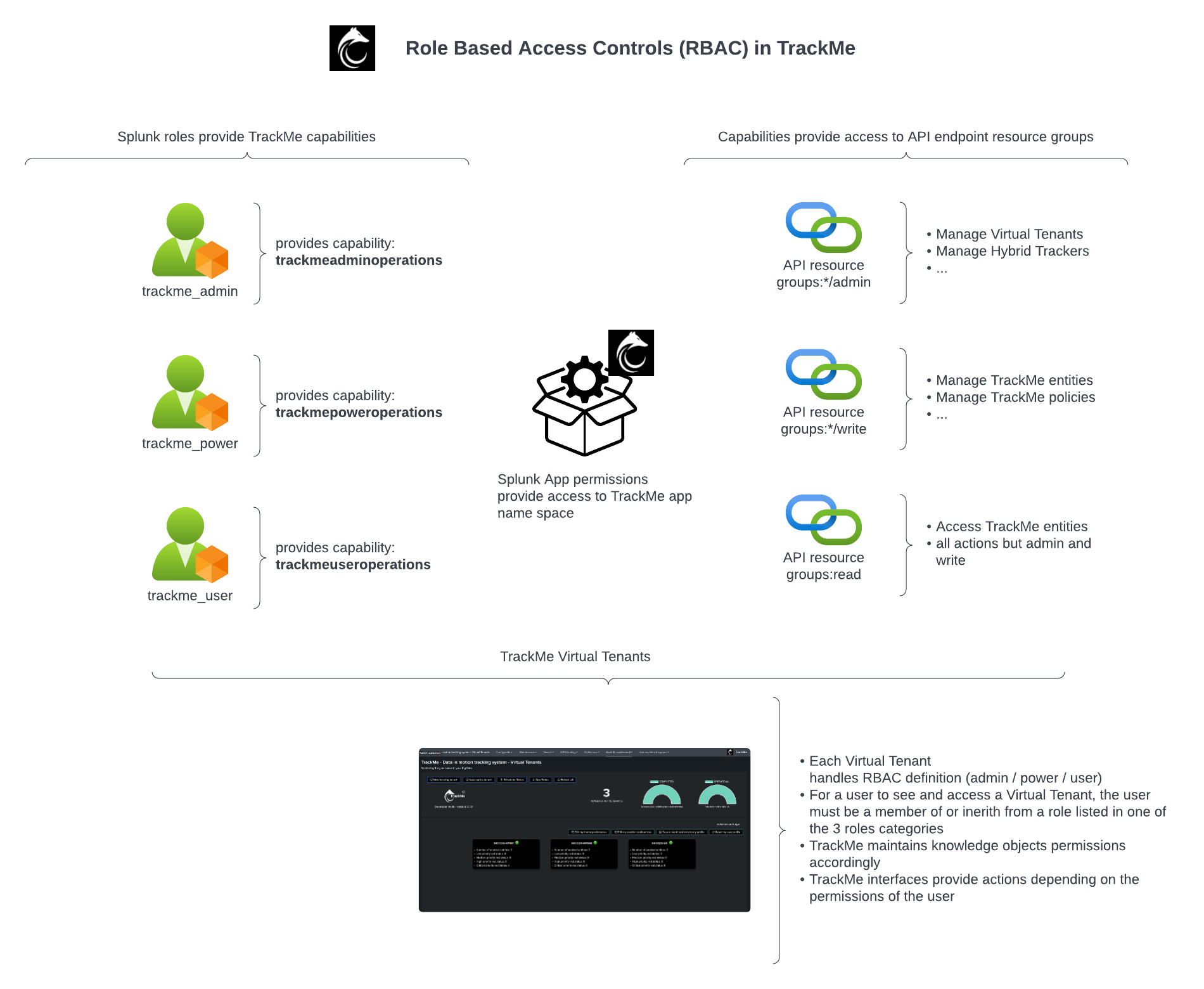
TrackMe uses a 3 RBAC levels schema, with the following built-in roles: trackme_user, trackme_power, trackme_admin.
Each of these roles provides a built-in capability (trackmeuseroperations, trackmepoweroperations, trackmeadminoperations) which allows access to the associated REST API endpoints.
Depending on the level of privileges, users will have access to different parts of TrackMe user interfaces; for instance, a read-only user will not have visibility of any administration-related shortcuts or entity edition buttons.
When migrating from a prior version, TrackMe will automatically assign the same permissions for existing tenants for the trackme_admin roles of the tenants to the trackme_power roles.
You can use TrackMe’s built-in RBAC re-assignment to update a tenant configuration according to your needs.
RBAC is also supported and required at the level of Splunk remote account.
Roles inheritance for TrackMe Virtual Tenants and Remote accounts is fully supported.
Introduction to RBAC in TrackMe
Role Based Access Control and Ownership management are supported and taken in charge natively, relying on a strict implementation of Splunk capabilities.
In short:
When a Virtual Tenant is created, TrackMe administrators can define target indexes for every type of data generated by TrackMe
Access to these indexes can be granted via Splunk Role Based Access Control
The Virtual Tenant knowledge objects permissions are configured during creation, allowing two types of access: administrative access and user access
When new knowledge objects are created for the tenant via TrackMe, the permission rules defined for the Virtual Tenants are applied automatically to these new objects
At any time, a TrackMe administrator can update the Role Based Access Control permissions for the Virtual Tenant; the tenant configuration will be updated and all existing knowledge objects for the tenant will be updated automatically
TrackMe built-in roles capability matrix
The following table summarizes TrackMe’s built-in roles, associated capabilities, endpoints access, and privileges categories:
Role |
Capability |
Endpoints root |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
trackme_user |
trackmeuseroperations |
all but write and admin |
allows read-only access in TrackMe |
trackme_power |
trackmepoweroperations |
*/write |
allows management of TrackMe entities but not the creation of new content (such as trackers) |
trackme_admin |
trackmeadminoperations |
*/admin |
allows content management such as the creation of tenants and trackers |
As a summary:
When defining your own roles integration, you can choose to have users being members of TrackMe built-in roles, or you can choose to inherit these roles into your own roles to grant TrackMe capabilities accordingly
A member of a role providing the trackmeadminoperations capability can create tenants and scheduled logics (trackers) even if the user’s Splunk permissions do not normally allow the creation of scheduled knowledge objects; this is made possible only in TrackMe for TrackMe context via TrackMe’s REST API and through elevation of privileges according to the user’s capabilities
If a user who does not own the trackmepoweroperations capability attempts to perform a write operation through an associated REST endpoint, Splunk will refuse access to this endpoint
Similarly, if a user who does not own the trackmeadminoperations attempts to reach any of the admin-related REST endpoints, Splunk will refuse access to the requested endpoint
Configuration user interface and RBAC requirements
TrackMe relies on the Splunk UCC Framework for the purposes of the configuration level backend; this is required to be able to leverage the configuration user interface for the purposes of RBAC re-assignment and ownership management.
The following capabilities are required:
list_settings
list_storage_passwords
admin_all_objects
These capabilities are required only for the configuration UI; these are not required for the creation and/or management of TrackMe knowledge objects (virtual tenants, trackers, …)
Typically, these capabilities are granted to Splunk administrators only, changes to the central configuration in TrackMe are not frequent actions and not part of the daily operations for TrackMe administrators.
Definition of RBAC and ownership at the creation phase of the Virtual Tenant
Hint
Preset RBAC for the tenant creation UI
You can preset values for the owner and roles when creating a new Virtual Tenant from the UI
Go to Configuration / General / RBAC: sharing, ownership and default roles
Defining RBAC when creating new Virtual Tenants:
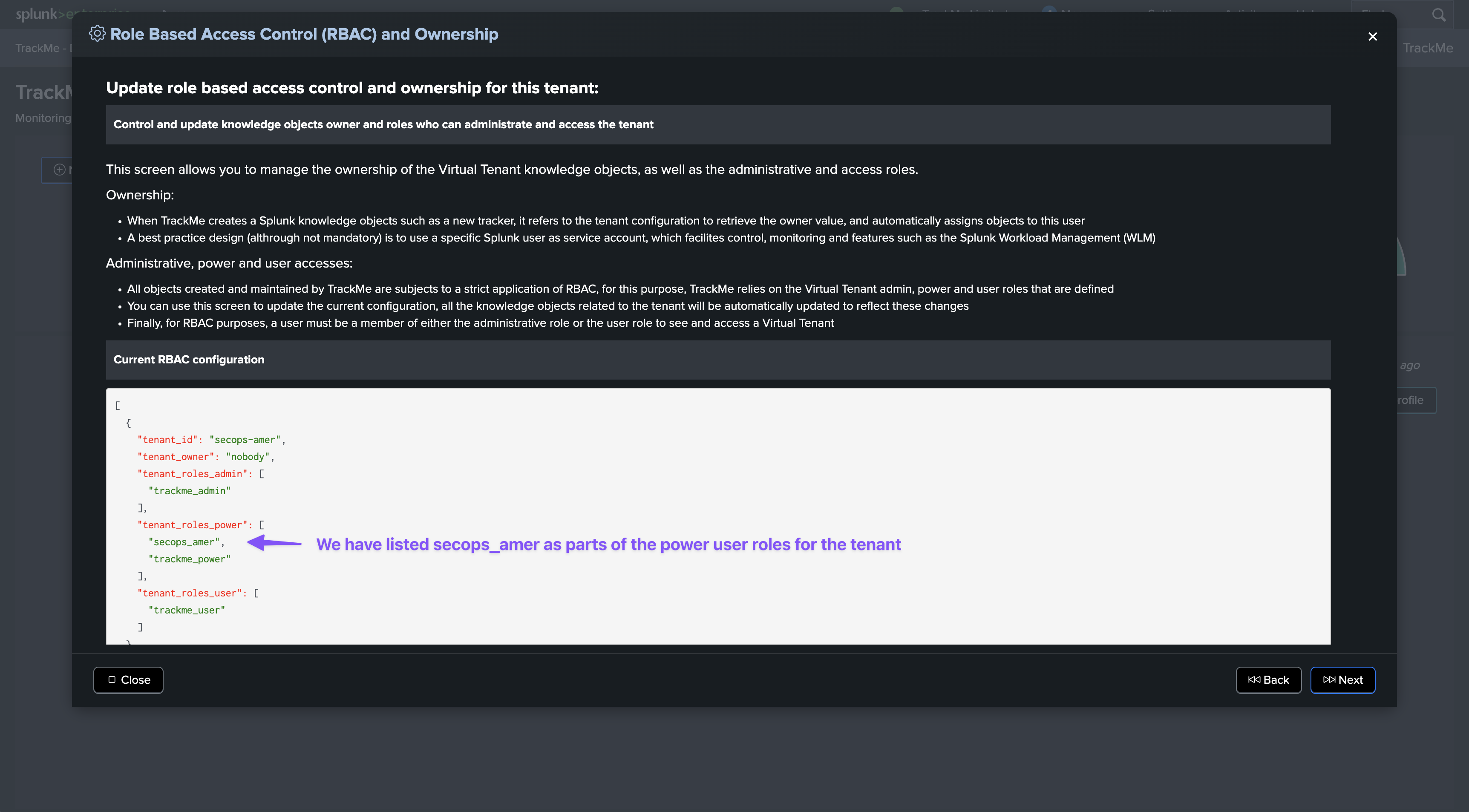
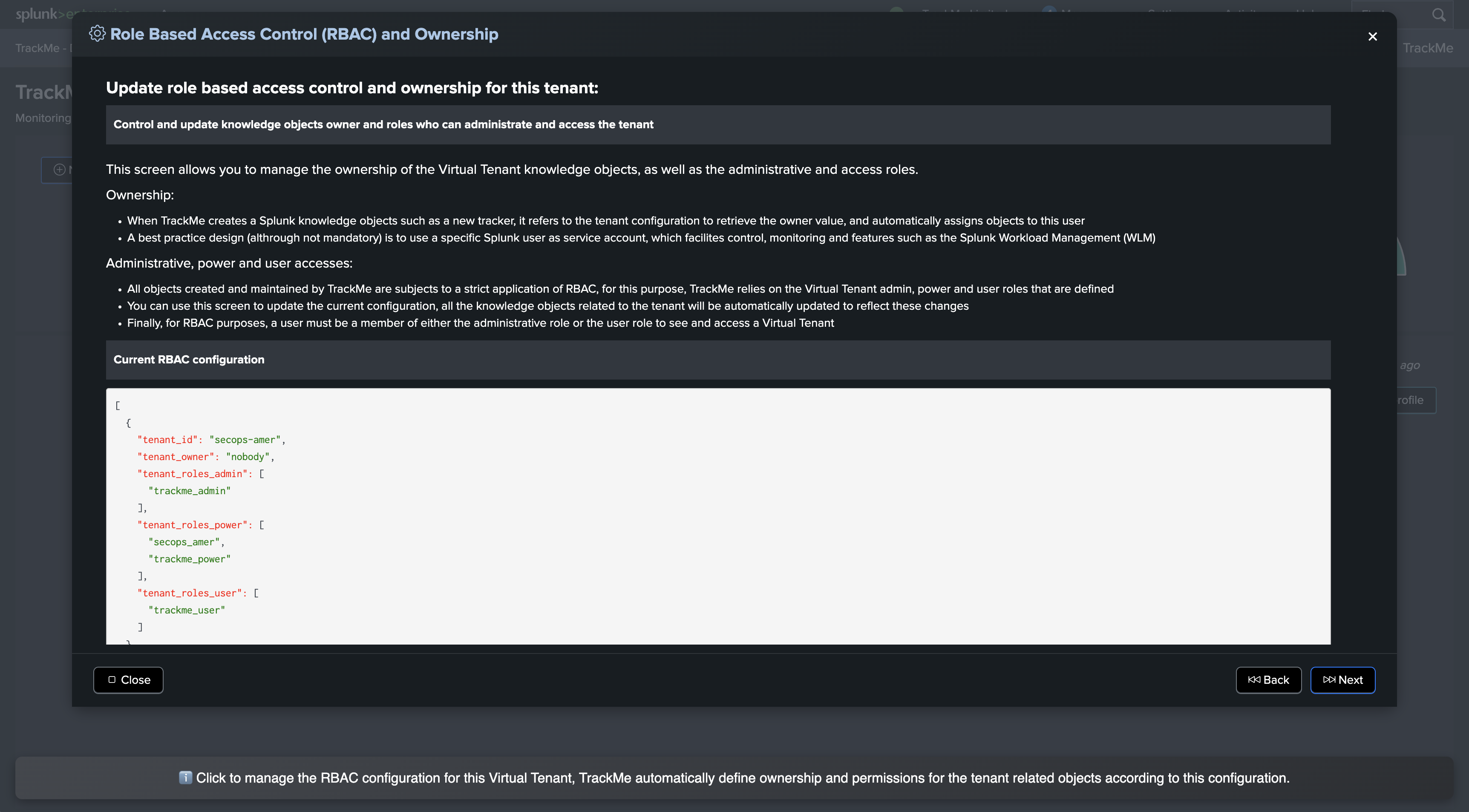
Once the tenant has been created, we can observe the permissions and ownership carefully defined by TrackMe:
Example: Defining role access for Virtual Tenants
This simple example shows how to filter and provide access to TrackMe Virtual Tenants depending on the user’s role.
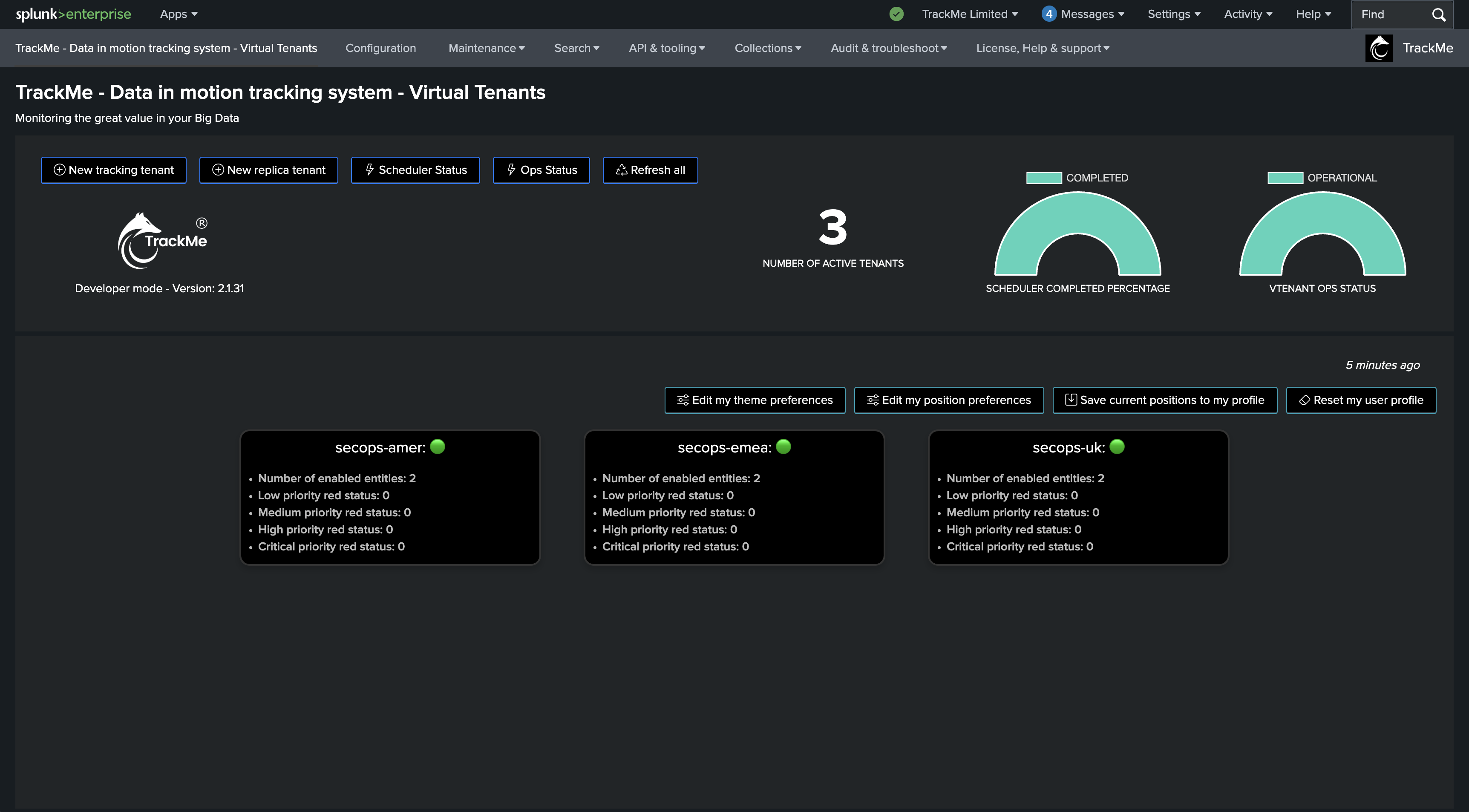
In this example, we have 3 Virtual Tenants:
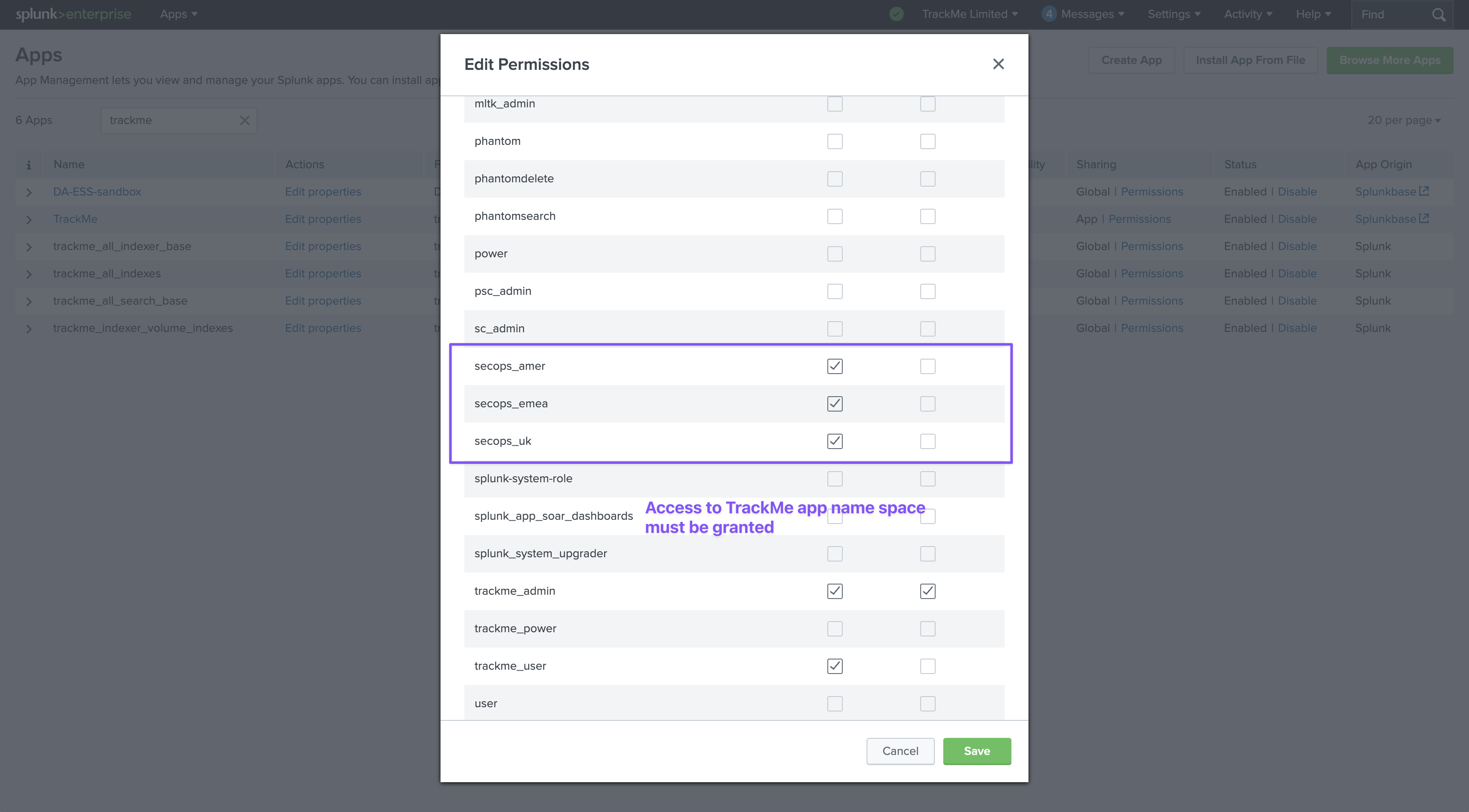
secops-emeawhich is meant to be dedicated to the EMEA security operations team, Splunk rolesecops_emeasecops-amerwhich is meant to be dedicated to the Americas security operations team, Splunk rolesecops_amersecops-ukwhich is meant to be dedicated to the UK security operations team, Splunk rolesecops_uk
A user connected as a TrackMe administrator will be able to access all 3 Virtual Tenants, however each Virtual Tenant is configured with a different role access:
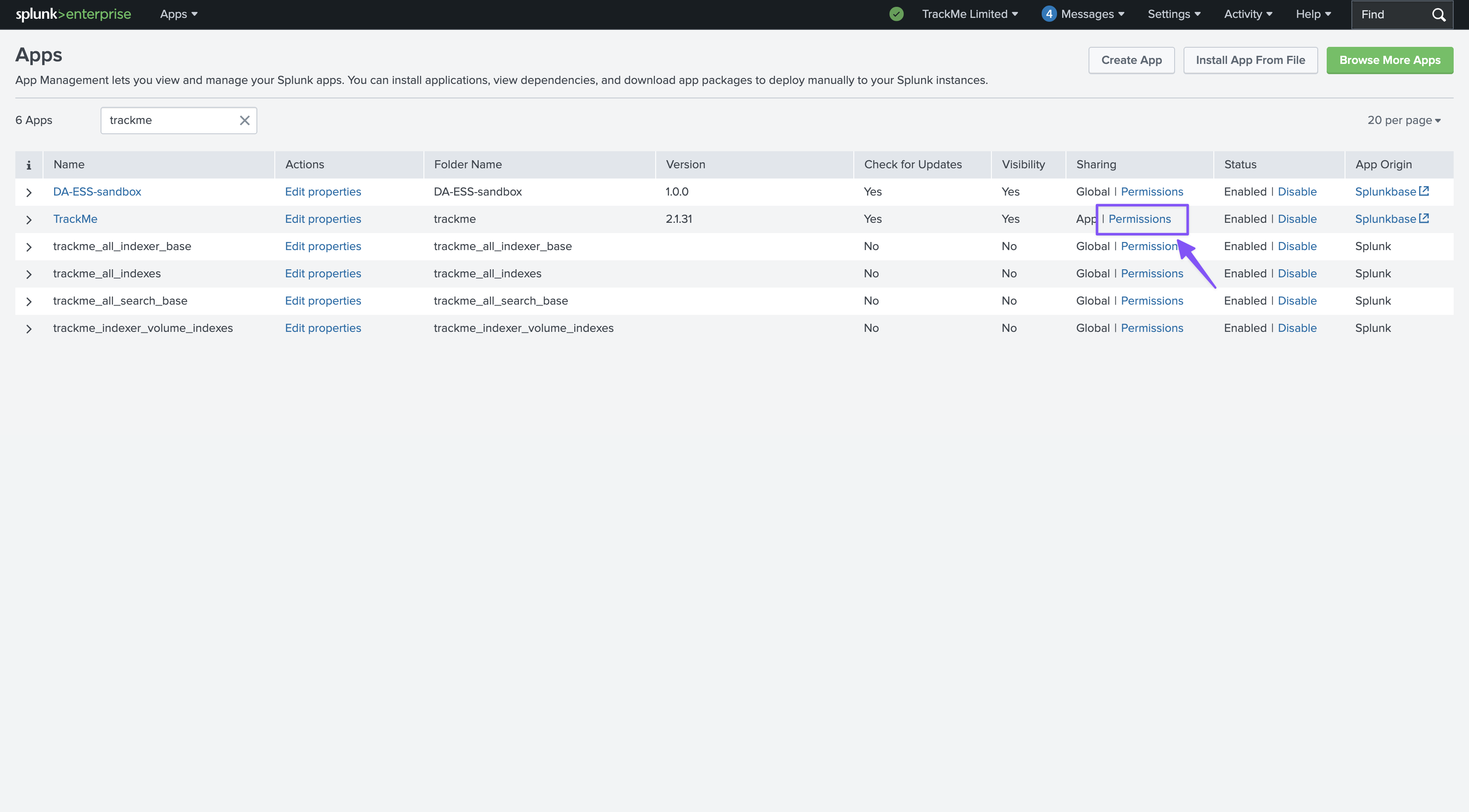
We must provide access to the TrackMe application name space for each of the roles:
Warning
role inheritance: if the user inherits from one of the 3 out of the box TrackMe roles, and the role is listed in the Virtual Tenant RBAC configuration, the user will be granted access to the Virtual Tenants
By default, when creating a Virtual Tenant it will list the 3 roles in each RBAC category
This means that if the user role we want to use to provide access to TrackMe inherits from one of the 3 out of the box TrackMe roles, and we will leave the default configuration, the user will be granted access to the Virtual Tenant and will see all Virtual Tenants.
To simply manage the RBAC configuration, make the wanted TrackMe capability native of the user role instead. (or remove the default configuration from the Virtual Tenant)
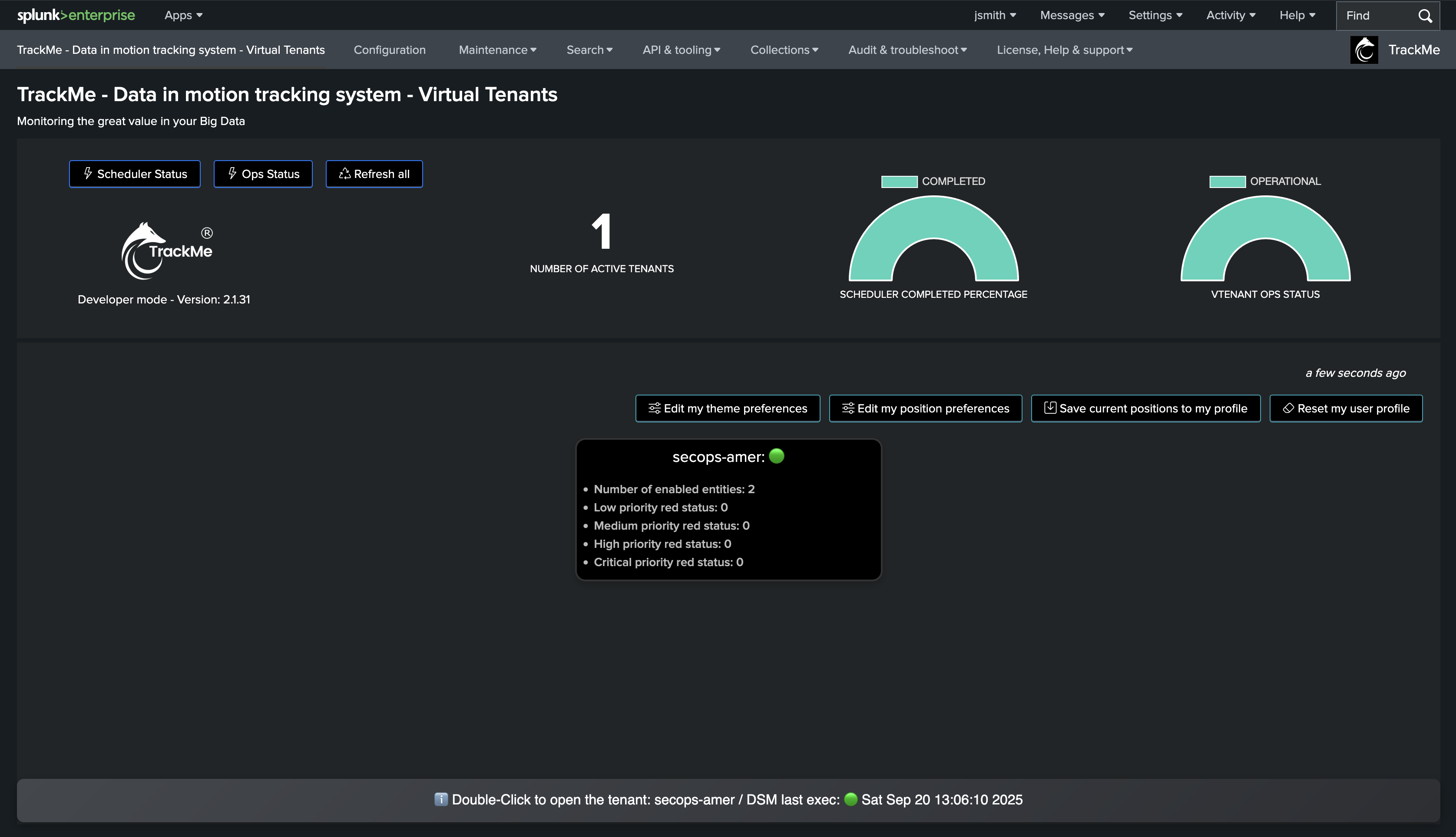
When a member of the roles we defined connects and accesses TrackMe, he will only see the Virtual Tenants he has access to:
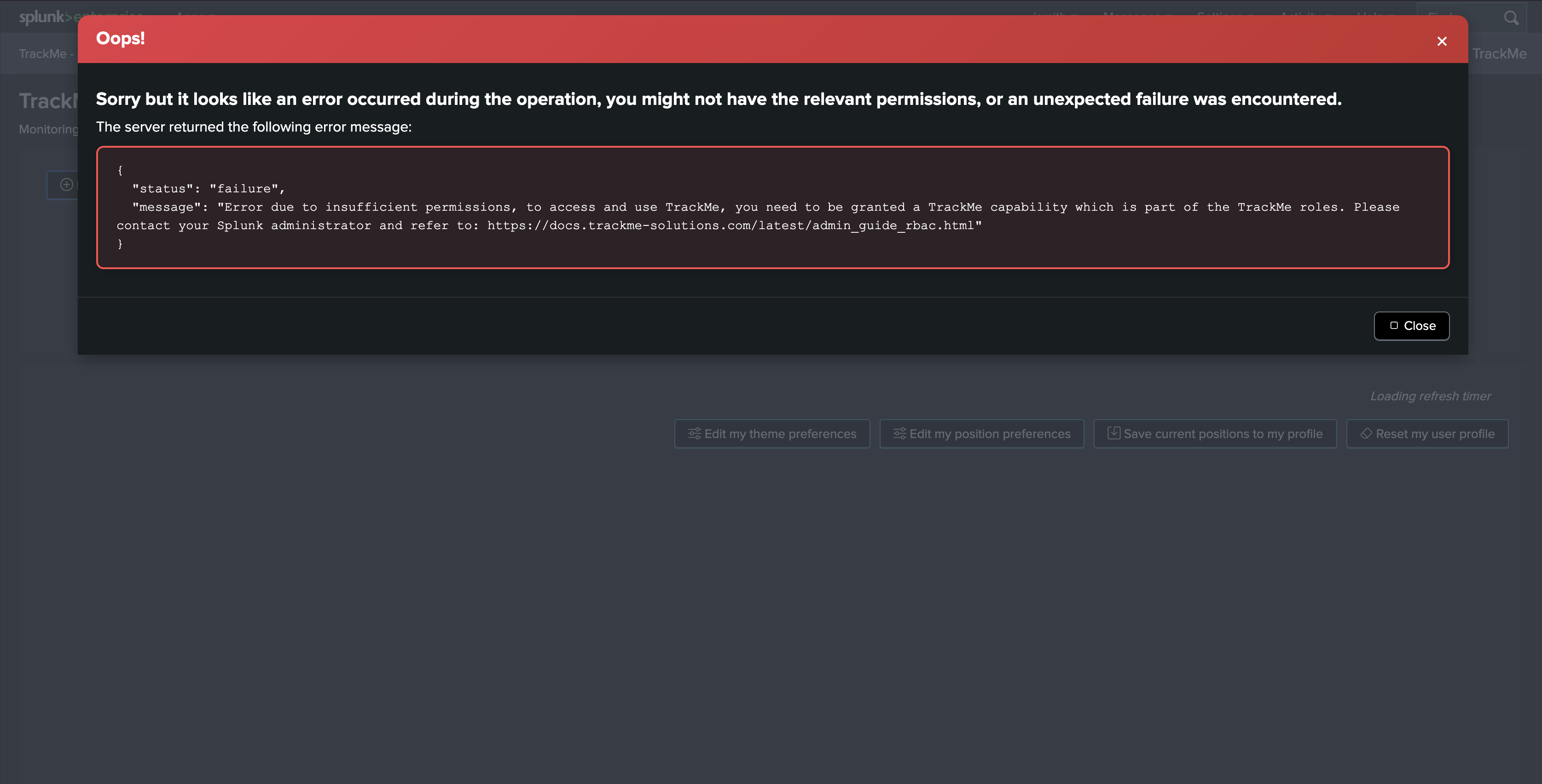
If by mistake, the user is granted access to TrackMe at the Splunk application level, but does not own the TrackMe capabilities needed, the following error screen will be shown:
In our example, the roles we have created are granted with TrackMe capabilities natively so the user can access resources as needed:
Updating RBAC policies and ownership assignment for an existing Virtual Tenant
TrackMe allows updating the Role Based Access Control policies as well as the ownership of an existing Virtual Tenant.
Updating RBAC through the Virtual Tenant user interface
Access the Virtual Tenant user interface, double-click on the tenant and access its administration screen:
Carefully update the ownership and/or RBAC policies; TrackMe will update the Virtual Tenant configuration, all of its knowledge objects will be re-assigned if necessary, and their permissions updated accordingly.
Updating RBAC through the REST API
You can equally update the RBAC policies and ownership through the REST API endpoint:
For instance, say we want to add an additional user role access siem_users to our tenant siem-quality-control, we could run:
| trackme url=/services/trackme/v2/vtenants/admin/update_tenant_rbac mode=post body="{ 'tenant_id': 'siem-quality-control', 'tenant_roles_admin': 'emea_siem_admin', 'tenant_roles_power': 'emea_siem_power', 'tenant_roles_user': 'emea_quality_control,siem_users', 'tenant_owner': 'srv-trackme'}"